How to Get Succession Certificate and Letter of Administration? - Succession Laws in Pakistan

How to Get Succession Certificate and Letter of Administration
How to Get Succession Certificate and Letter of Administration? Succession laws in Pakistan govern the distribution of a deceased person’s estate, ensuring their assets pass on to legal heirs. These laws are rooted in Islamic principles for Muslims, and in respective personal laws for non-Muslims. Two key legal instruments for managing the estate of a deceased person are the Succession Certificate and the Letter of Administration.
This blog post provides a detailed overview of succession laws in Pakistan, the difference between a succession certificate and letter of administration, and the complete procedure to obtain them through the courts or NADRA’s online system.
Understanding Succession Laws in Pakistan
In Pakistan, succession laws vary based on the religion of the deceased:
For Muslims, succession is governed primarily by Islamic law (Shariah) and codified under the Muslim Family Laws Ordinance, 1961.
For non-Muslims, succession is governed by their respective personal laws.
The Succession Act 1925 also plays a central role, especially for procedural matters such as issuance of succession certificates and letters of administration.
Succession determines who inherits, how much they inherit, and how assets should be transferred legally after a person’s death.
What is a Succession Certificate?
A Succession Certificate is a legal document issued by a civil court or NADRA (in certain cases) to the legal heirs of a deceased person. It enables them to:
Collect debts
Claim movable assets such as:
Bank balances
Stocks
Bonds
Insurance claims
Salaries or pensions
Vehicles
It does not cover immovable property like houses or land. For immovable property, you need a Letter of Administration.
What is a Letter of Administration?
A Letter of Administration is issued to legal heirs when a person dies intestate (without a will), and it covers:
Immovable property, such as:
Residential plots
Agricultural land
Houses
Commercial properties
It authorizes the appointed administrator (usually one of the legal heirs) to manage and distribute the deceased’s property among the heirs according to the applicable inheritance law.
Who Can Apply?
Legal heirs of the deceased are eligible to apply. These may include:
Spouse (widow or widower)
Children
Parents
Siblings (in certain cases)
Grandchildren (if their parents have passed away)
Heirs must provide proof of their relationship with the deceased and may be required to appear before the court or NADRA for biometric verification.
How to Get a Succession Certificate or Letter of Administration in Pakistan
There are two main routes to obtain a succession certificate or letter of administration in Pakistan:
1. Through NADRA Succession Facilitation Unit ( If NADRA Issue Decline Certificate)
2. Through Civil Court
Let’s go through both.
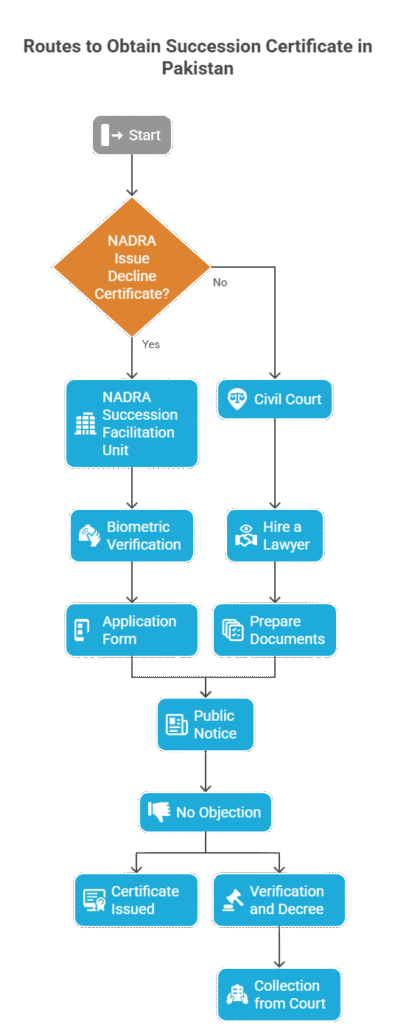
1. Procedure through NADRA’s Succession Certificate System
Launched in 2021, NADRA’s online Succession Facilitation Units provide a faster alternative for succession certificates involving moveable and immovable assets.
Where It Applies:
Only for Muslim Pakistani citizens
Only for moveable property
If no dispute exists among the heirs
Step-by-Step Process:
Step 1: Visit NADRA Facilitation Center
Locate your nearest NADRA Succession Center (available in major cities).
Step 2: Biometric Verification
All legal heirs must appear for biometric verification and provide CNIC copies and relationship proof.
Step 3: Application Form
An application is submitted detailing:
CNIC and death certificate of the deceased
List of heirs
List of assets
Step 4: Public Notice
NADRA issues a public notice in local newspapers for objections.
Step 5: No Objection
If no objection is received within 14 days, NADRA proceeds to issue the Succession Certificate.
Step 6: Certificate Issued
The certificate is issued digitally, with a QR code for verification by any institution.
Time Required:
Around 15 to 30 working days, faster than courts.
Cost:
NADRA charges a processing fee (usually Rs. 20,000–25,000)
If NADRA decline and Issue Decline Certificate on the any of the reason specified in law then you should approach the Civil Court.
2. Procedure through Civil Court
Step-by-Step Process:
Step 1: Hire a Lawyer
The process begins with engaging a qualified civil lawyer who can draft the petition and represent you in court.
Step 2: Prepare Documents
You will need:
CNIC of the deceased
CNICs of all legal heirs
Death certificate of the deceased
Heirship certificate (in some cases, from the local Union Council)
List of assets (bank accounts, vehicles, etc.)
Proof of relationship (like birth or marriage certificates)
Affidavits from legal heirs (on stamp paper)
Step 3: File Petition
Your lawyer files a petition under Section 372 of the Succession Act, 1925 in the relevant civil court.
Step 4: Public Notice
The court orders a public notice (usually in two national newspapers), inviting objections from the general public within 14 to 21 days.
Step 5: No Objection
If no objections are received, the case proceeds. All heirs may need to appear in court to give their statements.
Step 6: Verification and Decree
Once the court verifies everything and ensures there is no dispute, it issues a Succession Certificate or Letter of Administration.
Step 7: Collection from Court
You can collect the certified copies and present them to banks, vehicle registration departments, or property registrars.
Time Required:
Typically 30 to 90 days, depending on the workload and objections (if any).
Differences Between Succession Certificate and Letter of Administration
| Feature | Succession Certificate | Letter of Administration |
|---|---|---|
| Covers | All assets | All assets |
| Jurisdiction | NADRA or Civil Court | NADRA or Civil Court |
| Legal Basis | Succession Act 1925 | Succession Act 1925 |
| Appoints | Legal heirs as claimants | One heir as administrator |
| Who Issues | NADRA or Civil Judge | Civil Judge |
| Biometric Verification | Required (NADRA) | Not required (court route) |
Important Tips
If the deceased left a registered will, it must be produced, and the court will verify its authenticity.
In case of disputed inheritance, you will need to go through civil litigation.
Foreign Pakistanis can file for succession through their attorneys via a Special Power of Attorney attested by the Pakistani embassy.
Common Challenges in Succession Matters
Family disputes among heirs
Forgery or fake claims
Delays in newspaper publication
Disputed ownership of property
No bank records available
To avoid these, keep all property and financial documents updated, and ensure nomination forms in banks or pension departments are filled accurately.
Conclusion
Succession laws in Pakistan aim to provide a just and orderly distribution of a deceased person’s estate. Understanding the difference between a Succession Certificate (for movable assets) and a Letter of Administration (for immovable property) is crucial for legal heirs.
While NADRA has simplified the process for moveable assets, obtaining a letter of administration for immovable property still requires a court petition. With the right legal support and documentation, heirs can efficiently secure their rightful inheritance under Pakistani law.
Need Help?
If you need legal assistance in obtaining a succession certificate or letter of administration in Pakistan, our experienced lawyers at GNS Law Associates can help. Contact us today for a free consultation and let us make the legal process hassle-free for you.